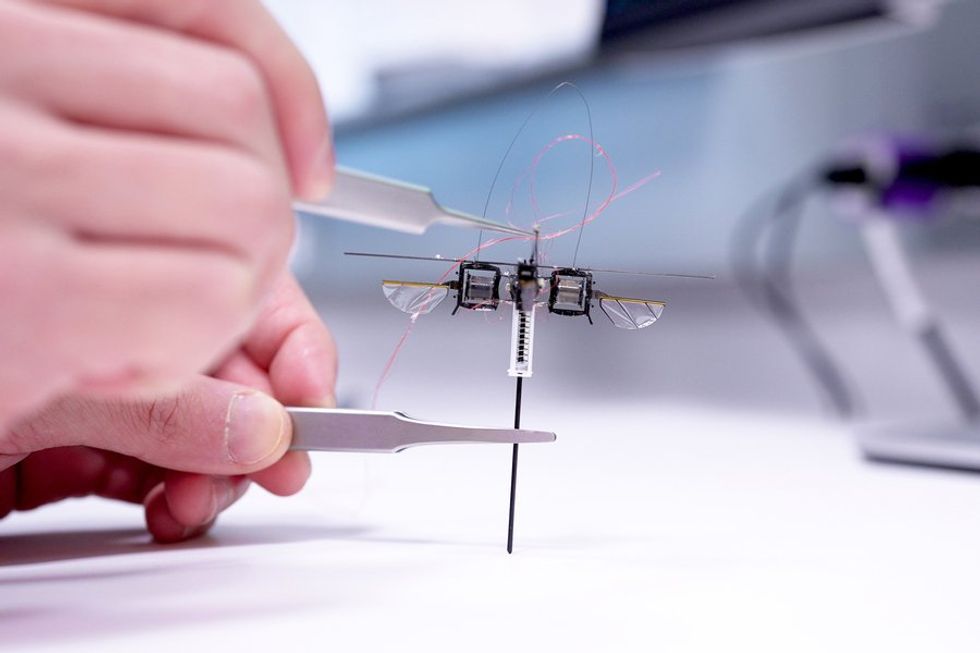
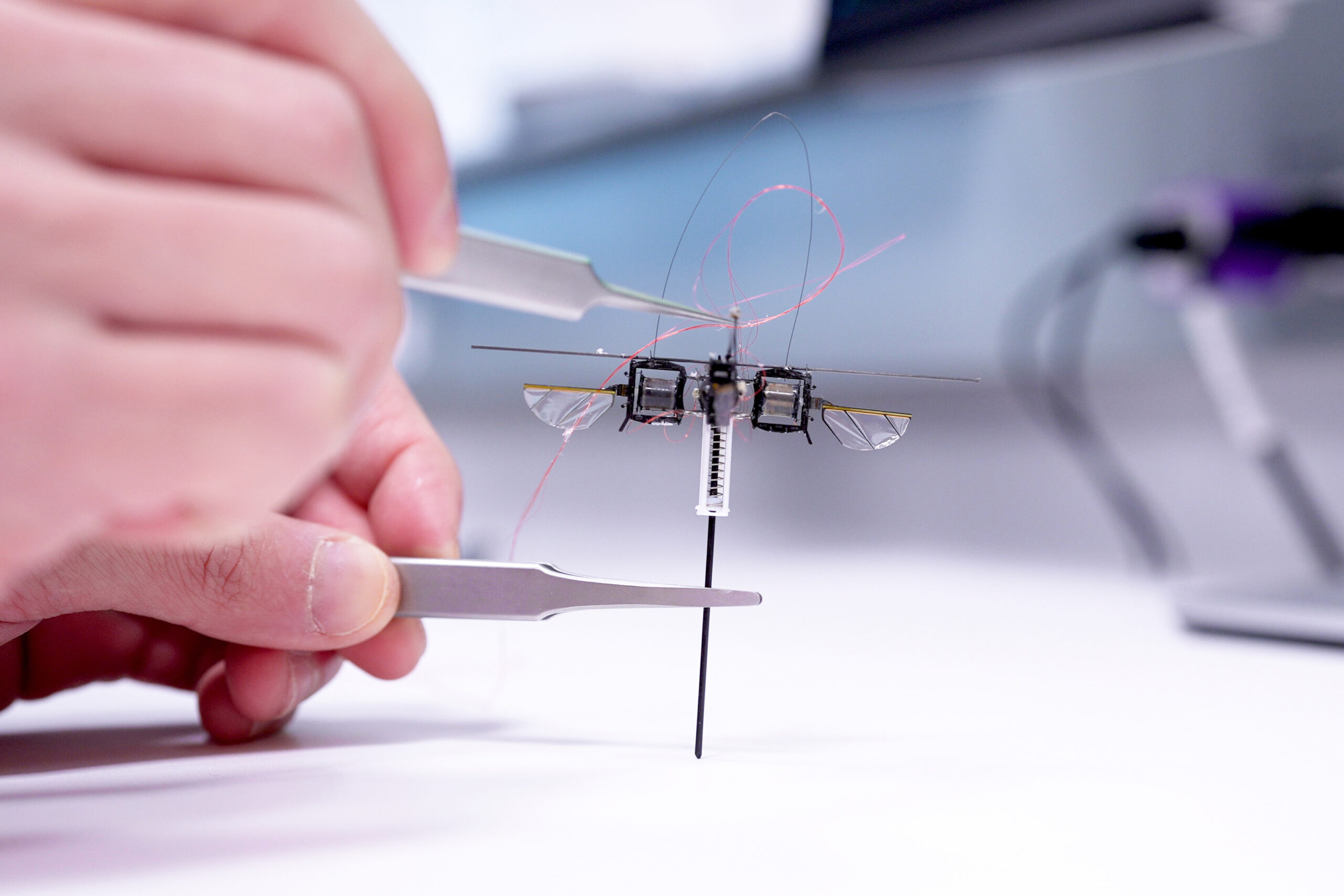
In today’s era, robots have become indispensable components of the technological revolution across diverse sectors. From household chores to large-scale manufacturing, robots have emerged to enhance productivity and streamline human existence.
There exist several classifications of robots, each meticulously designed to serve distinct purposes. In this comprehensive discourse, we will delve into the intricate realm of different robot types.
Types of Robot Products:
Non-Industrial Robots:
The realm of non-industrial or service robots encompasses a broad spectrum of applications, catering to professional, personal, and non-industrial requisites. This category encompasses a wide array of devices including home appliances, educational tools, entertainment gadgets, healthcare aids, and hospitality assistants.
Here are some key categories within this realm:
Home Appliances:
Robots in this category assist with various household chores, enhancing convenience and efficiency in daily routines. Examples include robotic vacuum cleaners such as Roomba, smart kitchen appliances that streamline cooking processes, and laundry folding robots that save time and effort.
Educational Tools:
In educational environments, non-industrial robots play a crucial role in teaching programming, problem-solving, and STEM concepts. Devices such as LEGO Mindstorms, Bee-Bots, and Ozobots engage students in interactive and hands-on learning experiences.
Entertainment Gadgets:
Robotic pets like Aibo and Pleo, along with interactive toys such as Cozmo, offer both entertainment and companionship. These robots often feature advanced AI and sensors that enable realistic interactions, making them particularly appealing to both children and adults.
Healthcare Aids:
In the healthcare sector, robots assist with surgeries, diagnostics, and patient care, significantly enhancing the efficiency and safety of medical procedures. Examples include the da Vinci surgical robots, exoskeletons for rehabilitation, and telemedicine bots that facilitate remote consultations. Additionally, robotic prosthetics and mobility aids are improving the quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
Hospitality Assistants:
Robots are increasingly being utilized in the hospitality industry to perform tasks such as room service delivery, cleaning, and customer interactions. For instance, Pepper, a humanoid robot, is often employed in hotels, restaurants, and airports to welcome guests and provide information.
As non-industrial robots continue to evolve, their applications across various sectors are expanding rapidly. Whether it’s a robot that helps you clean your home or a friendly chatbot addressing your queries, these technological marvels are playing a pivotal role in shaping our future. 🤖🌟
Unmanned Vehicles and Drones:
Under this category fall unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), colloquially known as drones. The terms “drone” and “UAV” are synonymous and interchangeable, denoting aerial apparatuses remotely controlled by humans or autonomously operated. These vehicles find utility across consumer and commercial domains, revolutionizing industries ranging from photography and surveillance to logistics and agriculture.
UAVs were initially developed for military missions that were considered too “dull, dirty, or dangerous” for humans.
Over time, their use expanded to various non-military applications, including:
Aerial Photography: Capturing stunning images and videos from the sky.
Precision Agriculture: Monitoring crops, assessing soil health, and optimizing farming practices.
Forest Fire Monitoring: Detecting and tracking wildfires.
Environmental Monitoring: Studying ecosystems, wildlife, and pollution.
Policing and Surveillance: Enhancing law enforcement operations.
Infrastructure Inspections: Checking bridges, power lines, and pipelines.
Product Deliveries: Exploring efficient delivery methods.
Entertainment and Drone Racing: Engaging in recreational activities.
Drones can be fully autonomous or controlled remotely by a human operator.
They often feature cameras for visual data collection and propellers for flight stability.
Future and Challenges:
The future of drone technology involves AI, machine learning, and IoT connectivity.
Challenges include privacy concerns and evolving regulations.
In summary, drones and UAVs are revolutionizing various industries, from photography to disaster response! 🤖🌟
Industrial Robots:
An industrial robot is a specialized robot system used for manufacturing and other industrial applications.
These robots are automated, programmable, and capable of precise movement along three or more axes.
Types and Features:
Articulated Robots:
These are the most common industrial robots.
Resembling a human arm, they have several degrees of freedom (joints) that allow a wide range of movements.
Articulated robots excel in tasks like welding, painting, and assembly.
Autonomous Robots:
These robots operate without human control.
Early examples, like Elmer and Elsie, were programmed to “think” autonomously, responding to light stimuli.
Autonomous robots can perform tasks independently
Cartesian Coordinate Robots:
Also known as rectilinear, gantry, or x-y-z robots. They have three prismatic joints for tool movement and three rotary joints for orientation in space.
Other types include cylindrical, spherical, SCARA, delta, and serial manipulators.
Applications:
Industrial robots perform tasks such as:
Welding: Joining metal parts.
Painting: Applying coatings consistently.
Assembly: Putting components together.
Pick and Place: Handling items on assembly lines.
Packaging, labeling, and palletizing.
Product inspection and testing.
They exhibit high endurance, speed, and precision, enhancing manufacturing efficiency
Global Impact:
As of 2022, approximately 3.9 million industrial robots operate worldwide1.
Their role in automation continues to grow, revolutionizing industries and shaping our technological future.
In summary, industrial robots are the workhorses behind modern manufacturing, contributing to productivity, quality, and innovation! 🤖🏭
Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial intelligence (AI) empowers computers and machines to emulate human intelligence and problem-solving capabilities. Tools such as ChatGPT and Gemini exemplify the application of AI in various domains, facilitating tasks ranging from natural language processing to data analysis and decision-making.
AI enables computers and machines to simulate human intelligence and problem-solving capabilities.
It encompasses a wide variety of technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP).
These technologies empower machines to perform tasks like recognizing speech, making decisions, and identifying patterns.
Real-World Examples:
You’ve likely interacted with AI-powered services or devices:
Recommendation Systems: Algorithms suggest movies, songs, or products based on your preferences.
Navigation Apps: They find the fastest route to your destination.
Language Translation: AI translates text from one language to another.
Types of AI:
Narrow AI (Weak AI): Specialized for specific tasks (e.g., chatbots, image recognition).
General AI (Strong AI): Mimics human cognition across various domains (still theoretical).
Benefits:
Efficiency: AI automates repetitive tasks.
Precision: It can analyze vast amounts of data quickly.
Innovation: AI drives advancements in medicine, finance, and more.
Dangers:
Bias: AI systems can inherit biases from training data.
Job Displacement: Automation may replace certain jobs.
Ethical Concerns: AI decisions impact privacy, security, and fairness.
In summary, AI is a powerful field that continues to shape our world, from virtual assistants to self-driving cars! 🤖🌟
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4.8 / 5. Vote count: 4
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?